Welcome to the complete beginners to advance NumPy library Guide. In this article, we explain step by step so you don’t need any previous knowledge of NumPy.
Keep reading,
Before we explain NumPy first understands what is an array.
What Is An Array?
The array is a collection of elements with the same data type stored in contiguous memory locations. It is a simple data structure when you access each data using the indexing method. The first items store 0 indexes and the second items store 1 index and so on. The array is a mutable data structure meaning it must change value.
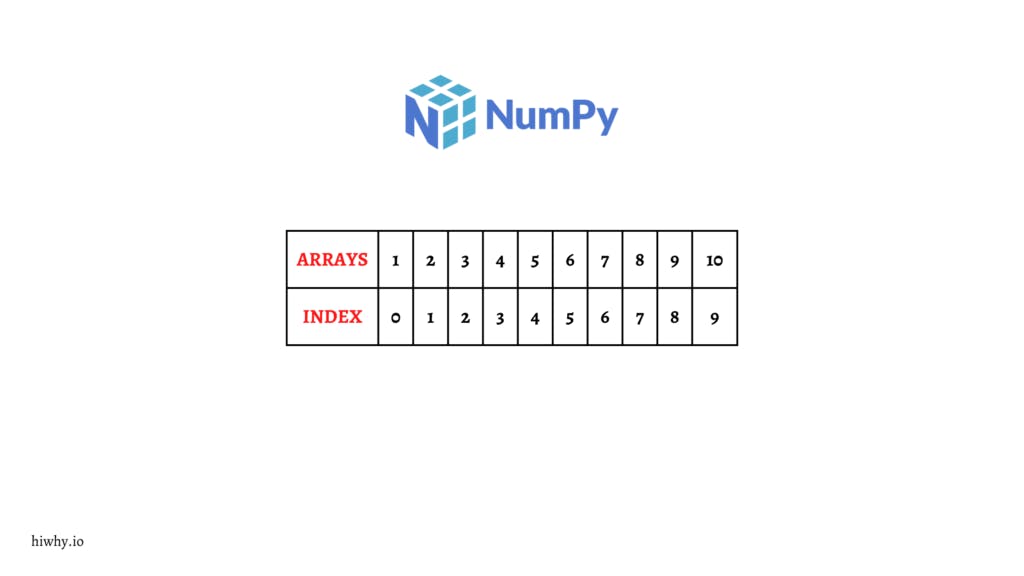
array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] # You think how many index have this array
print(array) ## print whole array
# Output >>> [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print(array[8]) # get only single value
# Output >>> 9
# how many indexes have 8 indexes have because start with 0
## Change value
array[0] = 10 ## replace 1 value to 10 value mean array data also changed.
print(array) # Notice first element changed
# Output >>> [10, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
What Is NumPy Array
NumPy( Numerical Python ) is an open-source array library in Python, creates in 2005 by Travis Oliphant. This library is used for converting anything into numbers. NumPy uses almost every field of science and engineering. Here is a list of people who use this library beginner coders, experienced researchers, top industrial researchers, data science engineers, Machine learning engineers, Artificial Intelligence developers, and so on.
Why NumPy Not Use Python
NumPy( Numerical Python ) is an open-source array library in Python, creates in 2005 by Travis Oliphant. This library is used for converting anything into numbers. NumPy uses almost every field of science and engineering. Here is a list of people who use this library beginner coders, experienced researchers, top industrial researchers, data science engineers, Machine learning engineers, Artificial Intelligence developers, and so on.
What Are The Advantages Of NumPy Over Python List
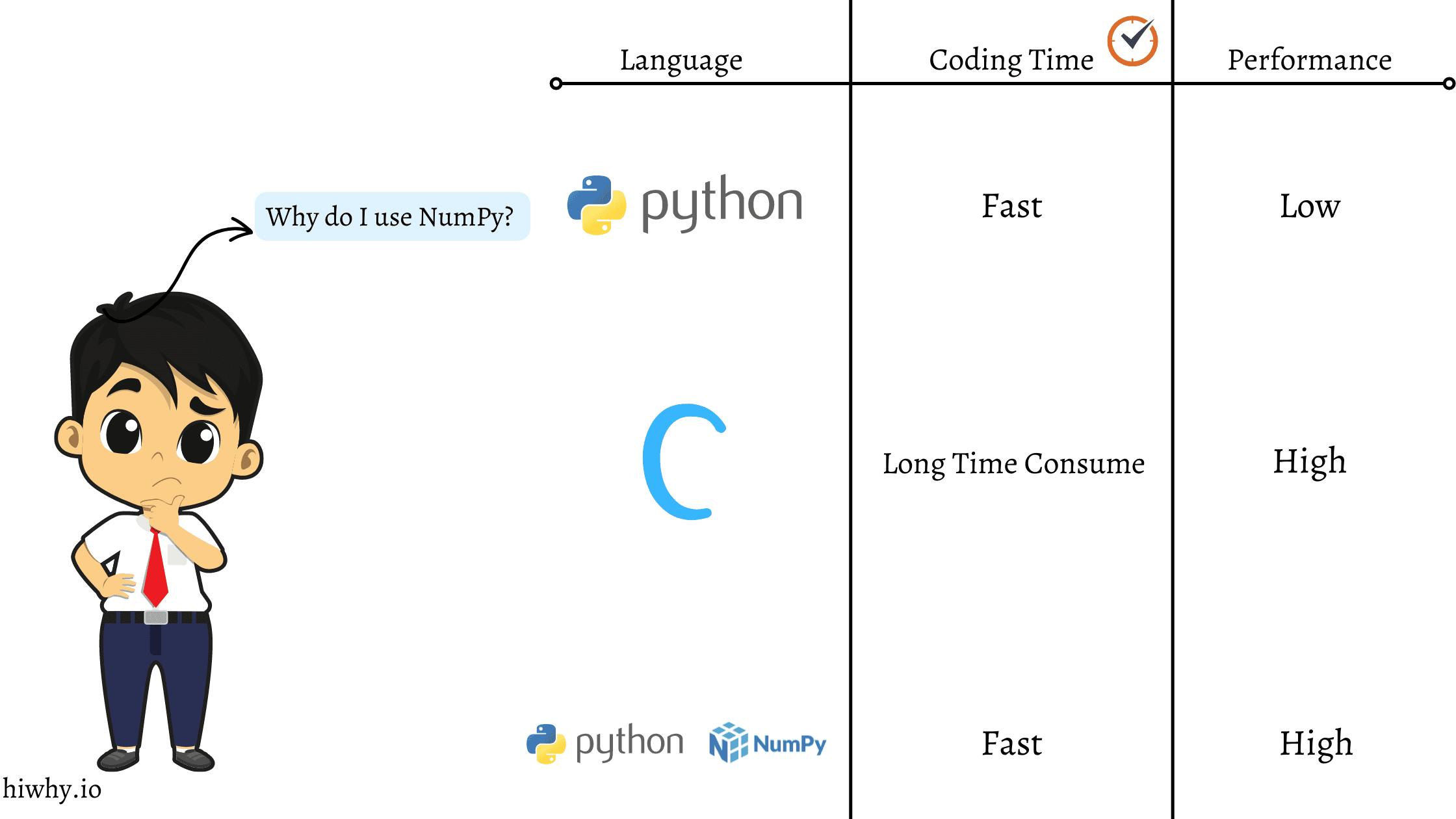
You can calculate numbers using a pure Python programming language. At the beginning of your journey DataScience, And you think it is fast but after, you work large dataset this time you notice Python code is slow. This reason DataScience professionals do not use Python.
Let’s understand why NumPy you use and what are the benefits of using NumPy.
The number one reason people use NumPy is that it’s fast ( 10* time fast compared to Python ). Because NumPy is built on the backend of another fastest programming language C.
Below are some of the list benefits of using NumPy.
Speed – NumPy is built on top of the C programming language, meaning NumPy writing C programming language. And remember C is the firstest programming language in the world. So when you use NumPy backend, run C code. So your code runs nanosecond. And that is the power of speed. But when you use python code at that time this code runs very slowly. Because python is not built for speed purposes, this language builds productivity purposes. That is why the data science community uses NumPy. Because they know how important speed is.
Fewer loops – Numpy helps you to reduce loops.
Clean code – When you use NumPy, that code is without loops. This means that code is like an equation and that time you quickly calculate anything. And one thing remembers coding is all about understanding one coder to another, not the machine.
Better quality – NumPy is open source and that library is used by millions of people. There are thousands of contributors working every day. They all have one mission: how to build NumPy fast, user-friendly, and bug-free. And one thing to remember open source means anybody has a chance to implement their idea. 💡
Keep Reading,
How To Install NumPy
If you are serious about data science, I recommend using Python scientific distribution. Follow this 2 step —
Download Anaconda on your computer. This library automatically downloads everything you need for your data science work.
Next is to download the PyThon programming language on your operating system.
# Type this command if you are using Anaconda
conda install numpy
# Type this comand if you are using Python
pip install numpy
# All of the command you run in your - Windows (Powershell), Linux, macOS(Terminal)
Optional tip 💡— If you don’t have to install Python on your computer, I suggest using the Anaconda distribution. The good thing about this distribution is, that you don’t need to worry about installing one by one your data science library on your computer. This distribution is an automatic download for you —Is this reason all of the data scientists use.
How To Use NumPy In Jupyter Notebook
If you are using NumPy the first step is to, import NumPy into your notebook ( Jupyter notebook or Google colab or if you use any code editor like VS Code ).
import numpy as np
# np is short form usning NumPy
Now it’s time know more information arrays
In this section, I am cover this topic — What is ( 1D array, 2D array, Ndarray, Vector, Matrix, Tensor ) ?
When you first data science comes, you hear this “ndarray”, but what does it mean? ndarray is a short form ‘N – dimension array’.
What Is An Ndarray NumPy
NumPy Array objects are called ndarrays. The n-d array is a multidimensional container of items this container is always fixed in size and same data type. The array number of dimensions of an item is defined by shape, this tuple of Non-Negative numbers specifies the size of each dimension.
N- dimension array means — an array with any number of dimensions. This array could be a 1D array, 2D array, and so on.
1D array — This array means an array with one dimension. 1d array is also called a vector.
2D array — Array with 2 two dimensions. 2d array is also called matrix.
Tensor — Array with 3D or higher dimensions, this is called a Tensor.
See the below code, so you can understand better.
# This is a 1D array >>> also called Vector.
first_array = np.array([1, 2, 3])
# This is a 2D array >>> also called matrix.
secound_array= np.array([[1, 2.0, 3.3],
[4, 5, 6.5]])
# This is a 3D array >>> also called tensor.
third_array = np.array([[[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]],
[[10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18]]])
Check Array Shape, Number Of Dimension, Datatype Or Type
# Check the first_array - Shape, Number of dimensions, DataType, Which type of array
first_array.shape, first_array.ndim , first_array.dtype , type (first_array)
# Output >>> ((3,), 1, dtype('int64'), numpy.ndarray)
# Let's understand one by one code meaning
# .shape >>> what is your shape of array ([1 , 2, 3 ]) - 3 shape
# .ndim >>> mean how many dimension have in your array ([1, 2, 3 ]) - 1 dimension
# .dtype >>> which dataType in your array ([1, 2, 3 ]) - int64
# type >>> this function check which type of array ([1, 2, 3 ]) - ndarray
# Check the secound_array- Shape, Number of dimensions, DataType, Which type of array
secound_array.shape, secound_array.ndim , secound_array.dtype , type (secound_array)
# Output >>> ((2, 3), 2, dtype('float64'), numpy.ndarray)
# Check the third_array >>> Shape, Number of dimensions, DataType, Which type of array
third_array.shape, third_array.ndim , third_array.dtype , type (third_array)
# Output >>> ((2, 3, 3), 3, dtype('int64'), numpy.ndarray)
# Now check all arrays one boy one
first_array
# Now check all arrays one boy one
first_array
third_array
Now see what the image looks like – the NumPy array. Because we are human beings understand better when seeing visuals.
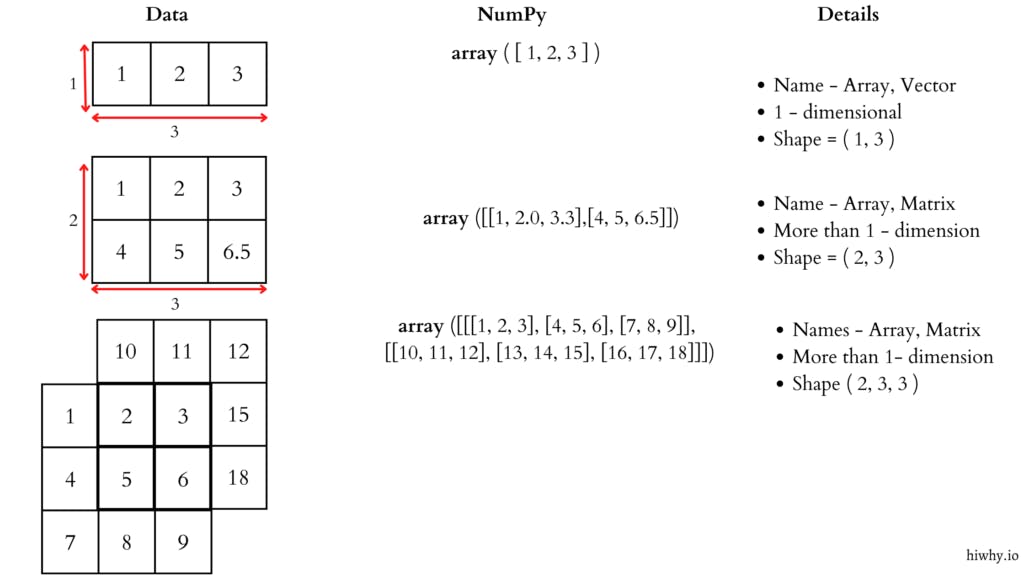
Important Points To Remember — NumPy Array
Array — A list of numbers can be any multi-dimension.
Scalar — This is a single number. Example – ( 3 ).
Vector —This is a list of number with 1 dimension .Example – ( [ 3, 6 , 9 ] ).
Matrix — This is a multidimensional array. Example – ( [ [3, 6, 9 ], [12, 15, 18] ] ).
How To Create A Array With NumPy
Creating array NumPy is very straightforward, just use this function np. array ( )
# The first step is to import numpy >>> So we can use
# np is short form NumPy
import numpy as np
first_array = np.array ([1, 2, 3 ])
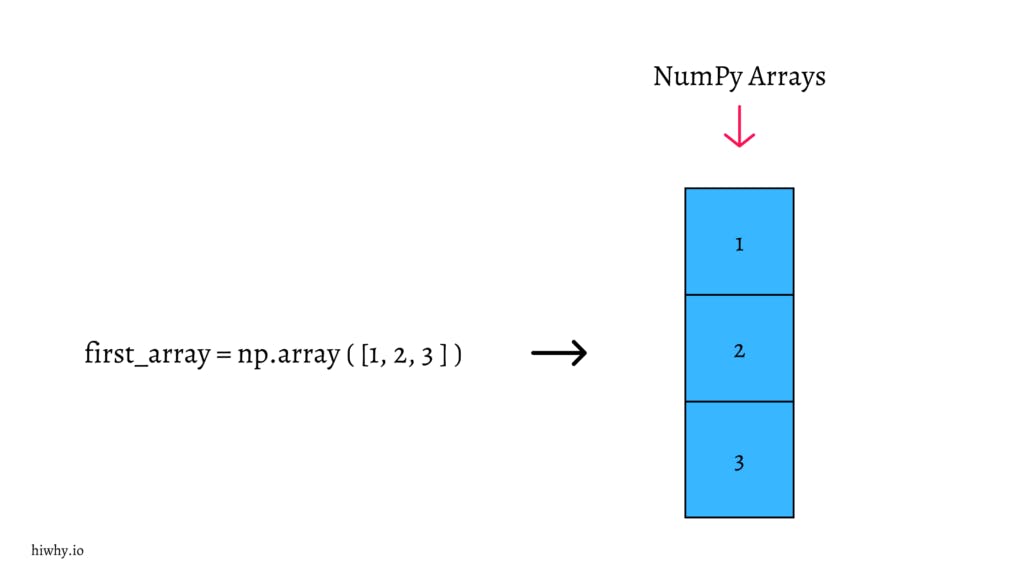
Now it’s time to create an array in your favorite number ( this is your homework )
my_faviourte_number = np.([ ])
# Fill this code and try what you learn
Keep Reading 👨💻
# Create an easy array [ ]
easy_array = np.array ([3, 6, 9 ]) # i use 369 because this is my lucky number!
easy_array
# Output
# array([3, 6, 9])
Check The Data Type Of NumPy Array
easy_array = np.array ([3, 6, 9 ])
easy_array.dtype # dtype is a keyword used to check which dataType your array
# output
# dtype('int64') # this array is a int (integer) dataType
# Now check some of the examples this array
easy_array_2 = np.array ([1.3, 2.1, 3.6, 9.3 ])
easy_array_2.dtype
# Output
# dtype('float64')
Create NumPy Array All Zeros And Ones
In this section you learn. Create array full zeros and ones, this time we are using NumPy two function achive this task.
‘0’ time np. zeros
‘1’ time np. ones
See the code example below.
zeros_array = np.zeros([3, 3 ])
zeros_array
"""
output
array([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]]) """
# in Python single-line comment time use this >>> #
# multiline comment time use this >>> """ """
ones_array = np.ones ([3, 3 ])
ones_array
"""
output
array([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]]) """
Check the type of these two arrays ⬇
zeros_array.dtype , ones_array.dtype
# Or you can use this so you can understand better
print ("zeros array dataType is >>> ", zeros_array.dtype)
print ("ones array dataType is >>> " , ones_array.dtype)
# output
# zeros array dataType is >>> float64
# Ones array dataType is >>> float64
As you can see, the default dataType in NumPy is float64. However, you can change this data type. See the code below on, how you can change the data type.
change_dataType_ones_array = ones_array.astype(int) #Use.astype() method and pass what datatype you want
# Check dataType new array
change_dataType_ones_array.dtype
# Output
# dtype('int64')
Create A Range Of Values In NumPy array
range_array= np.arange(10, 60, 2 ) # arange(start, stop, step)
range_array
# Output
# array([10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42,
44, 46, 48, 50, 52, 54, 56, 58])
How To Create A NumPy Random Array?
Creating a random array in NumPy is very easy, just use one method and pass argumetn it’s done. See the code example below
i_create_random_array = np.random.randint(30, size=(6, 6))
i_create_random_array
"""
output
array([[ 9, 15, 10, 22, 28, 21],
[ 4, 5, 9, 9, 26, 22],
[19, 10, 6, 5, 9, 19],
[ 4, 18, 15, 23, 27, 27],
[28, 28, 13, 19, 12, 26],
[ 0, 29, 16, 26, 27, 16]])
"""
"""
Now understand the code -- You can create a random array using NumPy np.random.randint() method
- i_create_randoom_array — Variable
- np.random.randint — numPy method
- 30 — mean our array only chose 0 to 30 number random
- size — we set the size of our array
"""
Generate Random Float Numbers In NumPy
Creating floating random numbers in NumPy is very straightforward. But this time we are using np.random.random( ) method.
Note — Integer time use np.random.randint ( ) and floating time np.random.random ( )
np.random.random((6, 6))
"""
output
array([[0.94410661, 0.60306752, 0.43754077, 0.84980106, 0.96659874,
0.57034047],
[0.96158039, 0.00915763, 0.82205839, 0.76609297, 0.03427183,
0.72891057],
[0.56588571, 0.23505534, 0.01526105, 0.35148204, 0.496939 ,
0.40903131],
[0.96478435, 0.12196867, 0.61626564, 0.68228989, 0.24604873,
0.70822664],
[0.83393187, 0.17939234, 0.75682693, 0.81067594, 0.47703851,
0.76172832],
[0.37983857, 0.98855208, 0.77995213, 0.49788636, 0.77745592,
0.9235587 ]])
"""
How To Add, Remove, And Sort Array In NumPy
Adding and sorting NumPy is very easy. Because two methods have achieved this goal.
np.sort( )
np.concatenate ( )
i_am_learn_sorting = np.array ([10, 90, 9, 7, 8, 6, 50, 5, 12, 3, 92 , 88])
i_am_learn_sorting
# output
# array([10, 90, 9, 7, 8, 6, 50, 5, 12, 3, 92, 88])
# Apply np.sort( ) method
np.sort(i_am_learn_sorting)
# output
# array([ 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 50, 88, 90, 92])
Concatenate Multiple NumPy Arrays
Keep reading ,
first_array = np.array ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 ])
secound_array = np.array ([11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20])
np.concatenate ((first_array, secound_array))
"""
output
array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17,
18, 19, 20])
"""
How To Find Shape And Size Of A NumPy Array
Knowing which shape and size your array is very important. So in this section we cover how to find your array shape and size. In NumPy it is very easy because function have achive this goal.
Check How Many Dimensions Have In This Array
i_learn_ndim = np.array ([[[0,1,2,3],
[4,5,6,7]],
[[0,1,2,3],
[4,5,6,7]],
[[0,1,2,3],
[4,5,6,7]]])
Can you guess how many dimensions this array has, this is your question?
If you don’t know it’s ok, let’s see it in answer together.
i_learn_ndim = np.array ([[[0,1,2,3],
[4,5,6,7]],
[[0,1,2,3],
[4,5,6,7]],
[[0,1,2,3],
[4,5,6,7]]])
i_learn_ndim.ndim
"""
Output
3
3 dimensions of this array. Let's understand one by one
i_learn_ndim = np.array ([[[0,1,2,3], # first dimension
[4,5,6,7]],
[[0,1,2,3], # Secound dimension
[4,5,6,7]],
[[0,1,2,3], # Third dimension
[4,5,6,7]]])
"""
Check How Many Elements Have In This Array
i_learn_ndim.size
"""
Output
24
i_learn_ndim = np.array ([[[0,1,2,3], >>> Each dimension 8 element
[4,5,6,7]],
[[0,1,2,3],
[4,5,6,7]],
[[0,1,2,3],
[4,5,6,7]]])
# See our array of total 24 element have. Each dimension 8 element.
toal - ( 8 * 3 ) = 24 element
"""
Check The Shape Of The NumPy Array
i_learn_ndim.shape
"""
Output
(3, 2, 4)
3 Dimensions
2 Row
4 Elements
Let's understand one by one
i_learn_ndim = np.array ([[[0,1,2,3], >>> first dimension, 2 row , 4 Element
[4,5,6,7]],
[[0,1,2,3], >>> secound dimension, 2 row , 4 Element
[4,5,6,7]],
[[0,1,2,3], >>> third dimension, 2 row , 4 Element
[4,5,6,7]]])
"""
How To Change The NumPy Array Shape
If this is possible, the answer is yes. You can change the NumPy array shape. Because one function has achieved this goal.
See the code below as an example.
i_learn_reshape_method = np.array ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ])
i_learn_reshape
# Output
# array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
# Check the shape
i_learn_reshape_method.shape
# Output
# (6,)
Change the shape of this array ( i_learn_reshape_method )
change_shape = i_learn_reshape_method.reshape(2, 3)
change_shape
'''
Output
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
'''
# check the shape
change_shape.shape
'''
Output
(2, 3)
See the difference -
'''
An Important Point To Remember Shape In NumPy Array
Reshape means you change the shape of the array.
If you use reshape we can add or remove any dimensions or elements for this array.
But it requires the same elements in both shapes.
See the code example below.
array_one = np.array ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ])
array_one
# Output
# array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
# Check the shape
array_one.shape
# Output
# (6,)
change_shpae_array_one = array_one.reshape(2, 3)
change_shpae_array_one
'''
Output
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
'''
# Check the shape
change_shpae_array_one.shape
# Output
# (2, 3)
Here are the example below— two array is not same shape. 🔻
array_two = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
change_shape = array_two.reshape (2, 4)
change_shape
"""
Output
array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8]])
"""
# this is the wrong way to shape your array
this_is_wrong = array_two.reshape(3, 3)
"""
Output
cannot reshape an array of size 8 into shape (3,3)
Because >>> Your array 8 element and you change this array 2D array
3 element
this is require ( 3 * 3 ) = 9 Elements
"""
Note — When you using the reshape ( ) method ,this method gives you a new shape without changing the original data. See the below code example.
my_array = np.array ([1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 12, 15 ])
my_array.shape
# Output
# (9,)
# Apply the reshape method
apply_reshape = my_array.reshape (3, 3)
apply_reshape.shape
# Output
# (3, 3)
# check two array shapes and see if my original array is changed or not
print ("my_array shape is ", my_array.shape)
print ("apply_reshape array shape is ", apply_reshape.shape)
'''
Output
my_array shape is (9,)
apply_reshape array shape is (3, 3)
Our original array shape has not changed
'''
Keep reading,
Indexing And Slicing NumPy Arrays
You can index and slice NumPy arrays, this is not new, you can do it in another programming language.
Let’s begin,
See below code example,
numpy_array = np.array([1,2,3])
numpy_array [1] # Output 2
numpy_array [0:2] # Output array([1, 2])
numpy_array [1:] # Output array([2, 3])
numpy_array [-2:] # Output array([2, 3])
I know you don’t understand this. It’s totally fine because, first time everything is difficult. But after it’s easy. See the image below so you can understand it better.
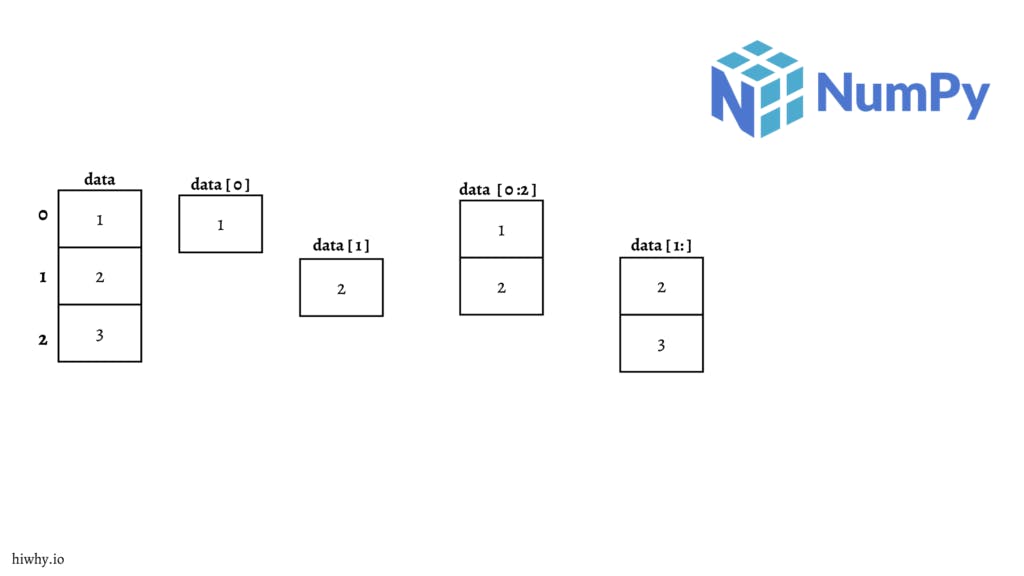
An important point to note —
In NumPy slicing means taking elements from one given index to another given index.
We pass a slice index like this [start: end ]. See code example below.
numpy_array = np.array([1,2,3])
numpy_array [0:2] # Output array([1, 2, 3])
# Let's see a big array so you can understand better.
big_array = np.array ([1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
big_array [0:11] # Output array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
We can also define an array like this [start: end: step].⬇
big_array = np.array ([1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
big_array [1:7:2] # Output array([2, 4, 6])
"""
Let's understand the code
big_array [1 "Start" : 7 "End" : 2 "Step"]
"""
big_array [0:9:3] # Output array([1, 4, 7])
If you don’t pass anything NumPy consider it’s 0
big_array = np.array ([1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
big_array [:11] # Output array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
big_array [:11:2] # Output array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
big_array [:9:] # Output array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
big_array [:9:3] # Output array([1, 4, 7])
Negetive Slicing NumPy Array
See the code below for examples on how you can negetive slices in the NumPy array. Negative slicing in NumPy is very easy but fast time it’s complex you think.
import numpy as np
array_two = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(array_two[-3:-1])
'''
Let's see how this code works
array_two = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) >>> negative time [ 7 is 0 - 1 is 6 ]
'''
Another time, see how [ Start: Stop: Step ] Work .
import numpy as np
step_array = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(step_array[1:5:2]) # Output [2 4]
print(step_array[1:7:2]) # Output [2, 4, 6]
How To Copy NumPy Array To Another Variable
Copy one array and store another variable is very easy, because in NumPy one method has achieved this goal. See the code example below.
my_array_one = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]])
my_array_one
'''
Output
array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12]])
'''
# Now use copy() method
copy_array_one = my_array_one.copy()
copy_array_one
'''
Output
array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12]])
'''
Now it’s time to learn some of the mathematics in NumPy. Don’t worry I am not discussing [EC^3 or Q2L^ ] this type of notation.
$$+-*/$$
We simply learn important ones.
addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and some
See the code below as an example.
We first created two arrays.🔻
first_array = np.array ( [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12] )
secound_array = np.array ( [14, 16 , 18, 20, 22, 24] )
first_array = np.array ([2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12])
secound_array = np.array ([14, 16 , 18, 20, 22, 24])
# Let's add +
first_array + secound_array
# Output
# array([16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36])
# apply the sum ( ) method
first_array = np.array ([2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12])
first_array.sum() # Sum method give you total sum element array
# Output 42
# let's learn Subtraction, multiplication, division ➖✖️➗
first_array = np.array ([2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12])
secound_array = np.array ([14, 16 , 18, 20, 22, 24])
first_array-secound_array # Subtration -
# Output array([-12, -12, -12, -12, -12, -12])
first_array*secound_array # Multiplication *
# Output array([ 28, 64, 108, 160, 220, 288])
first_array / secound_array # Division /
'''
Output array([0.14285714, 0.25 , 0.33333333, 0.4 , 0.45454545,
0.5 ])
'''
Let’s see one more useful mathematical function in NumPy 🔻
# In this code we learn how to use max (), min (), sum () this method
# we have a two array
one_array = np.array ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 ])
two_array = np.array ([12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21])
one_array.max()
# Output 11
two_array.max()
# Output 21
one_array.min()
# Output 1
two_array.min ()
# Output 12
one_array.sum()
# Output 66
two_array.sum()
# Output 165

Most Used NumPy Method
In this section, I cover the most useful methods in NumPy.
array_is = np.array ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 99, 9, 10, 11, 11, 13, 14,])
print_unique_value = np.unique(array_is)
print_unique_value
# Output
array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 99])
# np. unique — Return all the unique elements array
Note— NumPy is a big library, you don’t know anything and I don’t know. So when you are confused about something. This function helps you a lot help ( ), let’s say you don’t know what the sum ( ) function does. So your question is? how to know what this function does ?
See the code below for an example of how to use help( ) function in numpy. 🔻
help(sum) # help function retrun docstring
'''
Help on built-in function sum in module builtins:
sum(iterable, start=0, /)
Return the sum of a 'start' value (default: 0) plus an iterable of numbers
When the iterable is empty, return the start value.
This function is intended specifically for use with numeric values and may
reject non-numeric types.
'''
How To Save and Load NumPy Array
In this section we learn how to save and load arrays in numpy. This is a very important concept in data science. In NumPy saving and loading is very easy, because one function has achieved this goal. Keep reading,
array_one = np.array([11, 20, 30, 44, 56, 66, 96, 76])
# Let’s say you save this array on your computer.
array_one = np.array([11, 20, 30, 44, 56, 66, 96, 76])
np.save('I_save_array_one.npy', array_one)
"""
Note💡— When you save your array. Type this thing
— Your Filename.npy (Extension ) >>> npy extension is stand for numPy.
"""
How To Load Numpy Array (.NPY) File
i_load_my_array = np.load('I_save_array_one.npy')
# Check the array
i_load_my_array
# Output array([11, 20, 30, 44, 56, 66, 96, 76])
"""
Note💡— When you load your array.
Use this function — np.load( ‘Yourfile_name.npy’ )
"""
Save NumPy Array In CSV Format
csv_array = np.array ([1, 20, 21, 91, 99, 96, 94, 101])
np.savetxt('my_csv_array.csv', csv_array)
'''
Remeber- When you save your CSV format use this
np.savetxt ('Yourfile_name.csv', csv_array)
'''
# Load save array in your notebook
np.loadtxt('my_csv_array.csv')
'''
Note 💡- When you load your csv array, use this function
np.loadtxt('YourFile_name.csv')
'''
Hi, tell me about it in the comment section below this question. This is a question important to me.
Did I miss any important concepts in NumPy don’t cover in this article?
Which thing you don’t understand?
Is my explanation type easy or hard?
If you have any questions — Don’t wait, just ask.
If you want to learn more about Python another important data visualization library is Matplotlib. Read this article end-to-end guide.